CEBS Why is XBRL recommended to be used?
From XBRLWiki
Revision as of 17:19, 14 April 2010; Katrin (Talk | contribs)
(diff) ←Older revision | Current revision | Newer revision→ (diff)
(diff) ←Older revision | Current revision | Newer revision→ (diff)

Contribution dated 2009-12-23
ALL TOPICS ARE STILL ON DISCUSSION!
Contents |
Introduction
(To be completed)
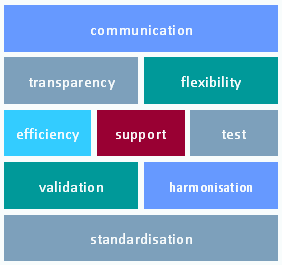
communication
- Single, XML-derived reporting standard
- Detailed understanding of data model
- Interoperability with existing XML schemas
- Several languages can be incorporated<
transparency
- Comparability of data across Europe
- Possibility of a faster exchange of information with regard to the financial crisis
- Versioning will be supported
- Open source
flexibility
- XBRL is extensible --> adaptation to national discretions
- Modularised architecture of XBRL
- Structural changes in the data are not reflected in the instance
efficiency
- Reduction of cost and time along the supply chain for financial information
- Eases the possibility of automation by supporting
- automated error detection
- versioning
- Time and cost saving for the reporting entity because of early responses
- One common format is more cost-effective than a numerous number of different proprietary formats
support
- Shifting of manual support to automated processes
- In-house developed systems can be replaced by �standardised market solutions
test
- XBRL reports can be easily tested before submission
- Transition process of a reporting entity could be supported by providing a test platform
validation
- Validation via standardised approaches
- Extensive possibilities for formula definitions
- Summarisation of formulas --> reduction of the amount of formulas
- No need for specific in-house solutions for the reporting entities
harmonisation
- Approach is in line with the reconciliation for an harmonised reporting in the EU
- Uniform validation rules can be used
- Allows cooperation on a unified data basis �(i.e. Colleagues of Supervisors)
standardisation
- Assures competitive capacity
- Eases the exchange with other European countries
- Enables the use of standardised technology
- Eases interoperability
- Minimises risks
- No other standardised business reporting standard exists